Chapter -3 | About Vagrant Installation and Setup & Vagrant Cheat Sheet
Vagrant is the command line utility for managing the virtual machines
What is Vagrant?
Vagrant is a tool for building and managing virtual machine environments in a single workflow. It makes life easier by lowering development environment setup time and increasing productivity.
Vagrant is the command line utility for managing the virtual machines. The following image shows the overview of vagrant.
Now let us understand this using a diagram
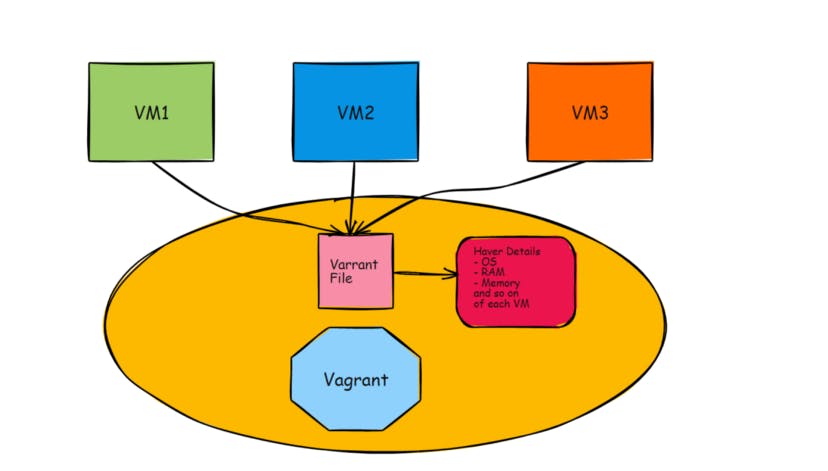
Managing various VM and configuring it is quite tedious. So using vagrant we can able to manage, configure and run multiple VM using a file known as “Vagrant File”.
A Vagrant file can keep the configuration of the VM such as OS, RAM, storage, and so on. when we run vagrant up command in a terminal, vagrant reads through the vagrant file and starts executing and creating VM according to the configuration.
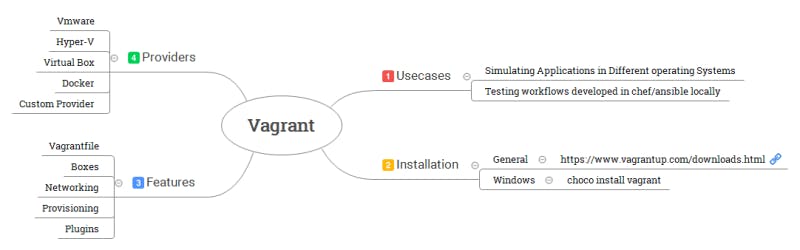
Features of Vagrant
Vagrantfile:
- A Vagrantfile is a configuration file for controlling virtual machine.
- It uses simple ruby syntax Refer here
- It contains all the necessary information needed for other user who wants to recreate the same VM.
- If the user needs to recreate the virtual machine created, then only Vagrantfile is shared
Boxes
- Boxes are the package format for Vagrant
- Boxes can be easily downloaded by using
vagrant box addcommand - Publicly available boxes are shared here.
- Every Box is restricted to run on supported providers. So while choosing the box checkwhether it matches your Provider(VirtualBox/Hyper-V/VmWare)
Networking
Vagrant supports 3 main types of networking
- Public Networking
- Private Networking
Port - Forwarding
Port-forwarding is the action of linking a port on your host machine to a port on the guest machine. Refer Link
- Private Networking allows the virtual machine to be accessed via private address. Refer Link
- Public Networking attempts to allow public access from outside your host machine (if your provider and machine will allow it) instead of just allowing access from inside the host machine. Refer Link
Provisioning
- Provisioning offers you the way to configure the virtual machine by executing Scripts or configurations. Refer here Provisioning happens in the following cases
- Executing
vagrant upcommand for the first time - Executing
vagrant provisioncommand - Executing vagrant
reload --provisioncommand
Plugins
- To change the way Vagrant does something or add additional functionality to Vagrant. this can be done via Vagrant plugins.
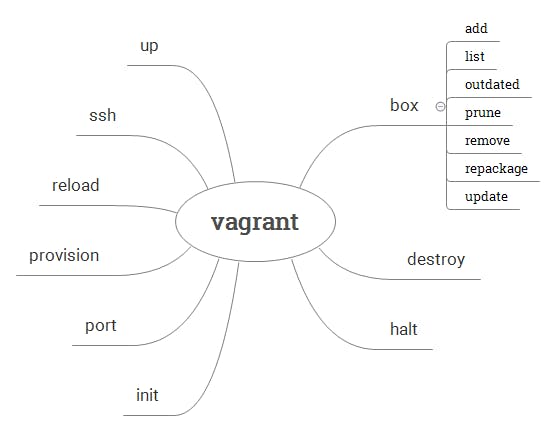
Creating a VM
vagrant initInitialize Vagrant with a Vagrantfile and ./.vagrant directory, using no specified base image. Before you can do vagrant up, you'll need to specify a base image in the Vagrantfile.vagrant init <boxpath>Initialize Vagrant with a specific box.
Starting a VM
vagrant upstarts vagrant environment (also provisions only on the FIRST vagrant up)vagrant resumeresume a suspended machine (vagrant up works just fine for this as well)vagrant provisionforces reprovisioning of the vagrant machinevagrant reloadrestarts vagrant machine, loads new Vagrantfile configurationvagrant reload provisionrestart the virtual machine and force provisioning
Getting into a VM
vagrant sshconnects to machine via SSHvagrant ssh <boxname>If you give your box a name in your Vagrantfile, you can ssh into it with boxname. Works from any directory.
Stopping a VM
vagrant haltstops the vagrant machinevagrant suspendsuspends a virtual machine (remembers state)
Cleaning up a VM
vagrant destroystops and deletes all traces of the vagrant machinevagrant destroy -fsame as above, without confirmation
Boxes
vagrant box listsee a list of all installed boxes on your computervagrant box add <name> <url>download a box image to your computervagrant box outdatedcheck for updates vagrant box updatevagrant box remove <name>deletes a box from the machinevagrant packagepackages a running virtualbox env in a reusable box
Saving Progress
vagrant snapshot save [options] [vm-name] <name>vm-name is often default. Allows us to save so that we can rollback at a later time
Tips
vagrant -vget the vagrant versionvagrant statusoutputs status of the vagrant machinevagrant global-statusoutputs status of all vagrant machinesvagrant global-status --prunesame as above, but prunes invalid entriesvagrant provision --debuguse the debug flag to increase the verbosity of the outputvagrant pushyes, vagrant can be configured to deploy code!vagrant up --provision | tee provision.logRuns vagrant up, forces provisioning and logs all output to a file
Plugins
vagrant-hostsupdater : $ vagrant plugin install vagrant-hostsupdater to update your/etc/hosts
file automatically each time you start/stop your vagrant box.
